Three Stages in Dissolution Testing
In the pharmaceutical industry, dissolution testing is a crucial step in the development and quality control of dosage forms. This testing helps to determine the rate and extent of drug release from a formulated product, which is essential for assessing the product's bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness.
During dissolution, drugs are tested to ensure that they meet the standards set by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. These standards mandate that a certain percentage of the active ingredient in a drug must be released within a specified time frame. Dissolution testing is also used throughout the product lifecycle to ensure consistent quality of the product. Manufacturers must monitor the dissolution performance of their products to ensure that they remain within acceptable levels over time and across batches.
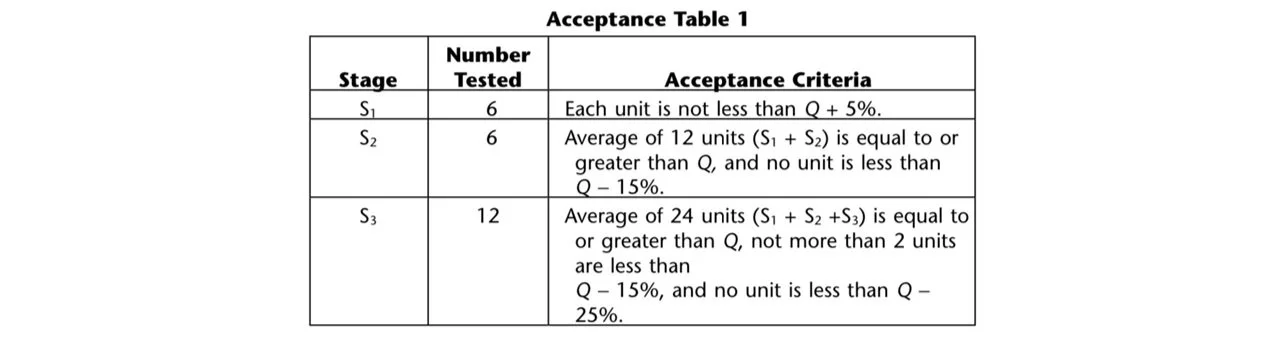
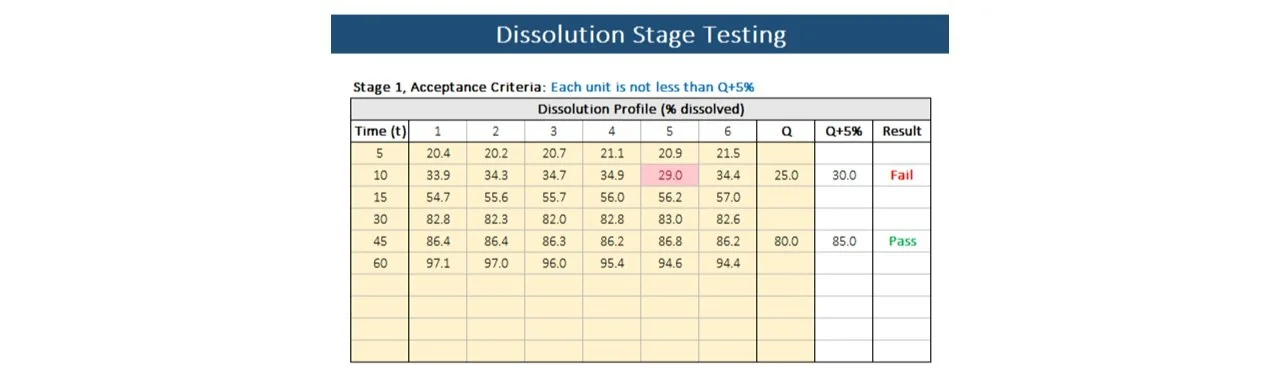
To meet dissolution requirements, the amount of active ingredient dissolved from the tested dosage units should align with the specifications outlined in Acceptance Table 1. It is necessary to continue testing through all three stages unless the results conform at either S1 or S2. The quantity, denoted as Q, represents the dissolved active ingredient as a percentage of the labeled content of the dosage unit. The values of 5%, 15%, and 25% in Acceptance Table 1 are also expressed as percentages of the labeled content, ensuring consistency with Q.
Reference: USP <711> Dissolution
Feeling overwhelmed? Simplify the process with our dissolution stage testing template. Quickly perform these calculations and make your life easier!
Do you have any questions or suggestions? Feel free to reach us by clicking here.