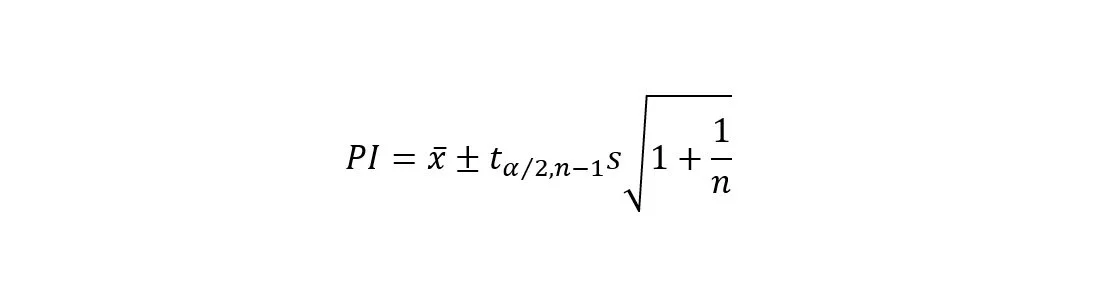Using Prediction Intervals to Set Specifications in Pharmaceutical Testing
Using prediction intervals for specification setting in the pharmaceutical industry involves employing statistical methods to estimate the range within which individual future observations are likely to fall. This is particularly relevant when setting specifications for drug product quality, ensuring that future batches conform to established standards. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use prediction intervals for specification setting in the pharmaceutical industry:
1. Define the Objective of Specification:
Clearly articulate the specific quality attribute or parameter for which you are setting specifications. This could include the % label claim of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), dissolution rates, or any other critical quality attribute.
2. Collect Historical Data:
Gather historical data on the quality attribute of interest. This dataset should be representative of the variability expected in the manufacturing process.
3. Choose Confidence Level:
Select the desired confidence level for the prediction interval. Common choices include 95% or 99% confidence levels, representing the percentage of intervals that will contain the true future observations.
4. Calculate Prediction Intervals:
Utilize the standard errors and the chosen confidence level to calculate the prediction intervals around the predicted values. The formula for the prediction interval for a simple linear regression model is:
Feeling overwhelmed? Simplify the process with our prediction interval calculator. Quickly perform these calculations and make your life easier!
5. Set Specifications:
The prediction interval provides a range within which future observations are expected to fall with the specified confidence. Use this information to set specifications that ensure the quality attribute meets the desired standards.
6. Validation and Adjustment:
Validate the prediction intervals using additional data, and be prepared to adjust specifications as more information becomes available. Continuous monitoring and adaptation to changes in the manufacturing process or raw materials are essential for maintaining product quality.
7. Document and Communicate:
Document the rationale behind the chosen prediction intervals and specifications. Clearly communicate these specifications to relevant stakeholders, including manufacturing teams and regulatory authorities.
Using prediction intervals for specification setting in the pharmaceutical industry is a proactive and statistically sound approach to ensuring product quality. By leveraging historical data, pharmaceutical manufacturers can set specifications that account for variability and uncertainties in the manufacturing process. Regular monitoring and validation of prediction intervals contribute to continuous improvement and the ability to adapt specifications based on evolving manufacturing conditions.